Parenting is crucial in shaping children’s lives, impacting their emotional, social, and academic development. Parents’ various ways with their children can be categorized into distinct parenting styles. But how do these styles distribute across different populations? One way to analyze this is through a parenting style repetition graph. This article explores the concept of parenting styles, explains what a repartition graph is, and discusses how it can help us understand different approaches to parenting.
What Are Parenting Styles?
Parenting styles are the strategies and methods parents use in raising their children. Experts typically categorize parenting into four main types:
- Authoritative: Characterized by warmth, structure, and open communication.
- Authoritarian: Emphasizes strict discipline and control, with little room for flexibility.
- Permissive: Involves a high level of leniency, with few rules or boundaries.
- Uninvolved: Marked by a lack of attention and engagement in the child’s life.
Each style has its impact on children, and understanding them is crucial for improving parenting practices.
What is a Parenting Style Repartition Graph?
A parenting style repartition graph is a data visualization tool that displays the distribution of different parenting styles across a given population. It helps illustrate how prevalent each style is, making it easier to analyze patterns and trends. These graphs are often used in research to better understand how various factors like culture, socioeconomic status, or education affect parenting practices.
Breaking Down the Four Major Parenting Styles
- Authoritative Parenting:
Authoritative parents combine love and boundaries. They are responsive to their children’s needs but also set clear expectations. In a repetition graph, authoritative parenting often occupies a significant portion due to its positive impact on child development. - Authoritarian Parenting:
This style focuses on obedience and discipline, with little room for debate. Authoritarian parents typically expect their children to follow rules without question. In a graph, this style may show a smaller or varying percentage, often associated with more traditional or rigid cultural backgrounds. - Permissive Parenting:
Permissive parents are lenient, allowing children to have a lot of freedom. While this can foster creativity, it can also lead to a lack of discipline. In the repetition graph, this style often shows up in lower numbers but may spike in certain populations or regions. - Uninvolved Parenting:
Uninvolved parents are emotionally distant and provide minimal guidance. This style has the smallest representation in most graphs, as it is generally seen as harmful to children’s well-being.
Benefits of Using Repartition Graphs for Parenting Styles
Graphs offer clear, visual insights into how parenting styles vary among different groups of people. With this data, parents and professionals can identify which styles are more common in certain communities or cultures. These graphs help with:
- Understanding dominant parenting approaches.
- Comparing individual parenting styles with societal norms.
- Observing trends or shifts over time.
How to Interpret a Parenting Style Repartition Graph
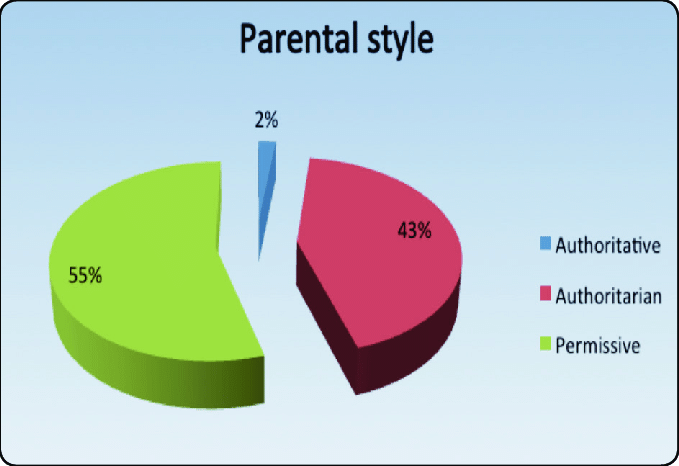
A parenting style repartition graph typically consists of four segments, each representing a different style. The larger the segment, the more prevalent that style is within the dataset. Here’s how to read it:
- Authoritative: Often the largest segment, indicating its widespread use and positive outcomes for children.
- Authoritarian: This may vary in size depending on cultural and societal factors.
- Permissive: Typically a smaller segment, showing its lesser adoption.
- Uninvolved: The smallest, often representing a minority of parents.
Key metrics to focus on include the percentage of parents using each style, changes over time, and any notable differences between regions or demographics.
Using Repartition Graphs for Self-Assessment
Parents can use repetition graphs to reflect on their parenting style. There are online tools and surveys available that can help you assess where you fall on the parenting spectrum. By visualizing this information, parents gain better clarity on how their style compares to others, encouraging self-reflection and improvement.
Parental Impact on Child Development Through Different Parenting Styles
The way parents raise their children significantly influences their future. For instance:
- Authoritative parenting often leads to well-adjusted, independent, and academically successful children.
- Authoritarian parenting may produce obedient children but can sometimes hinder emotional development.
- Permissive parenting fosters creativity but may result in behavioral problems.
- Uninvolved parenting has the most negative impact, often leading to emotional and academic challenges.
By observing these outcomes on a repartition graph, it becomes easier to understand the correlation between parenting style and child development.
Global Trends in Parenting Styles: What Repartition Graphs Reveal
Parenting styles can vary greatly depending on cultural, societal, and economic factors. For instance, authoritarian parenting may be more prevalent in cultures that value obedience and tradition, while permissive parenting might be more common in progressive societies. A global comparison of parenting style repartition graph reveals these trends, helping researchers understand how different environments influence parenting.
The Future of Parenting: Shifting Styles in Repartition Graphs
As the world changes, so do parenting styles. Modern challenges such as technology, work-life balance, and social media are reshaping how parents interact with their children. Repartition graphs can help predict these shifts, showing how trends in parenting styles are evolving.
Conclusion: Leveraging Data for Better Parenting
Understanding the distribution of parenting styles through a parenting style repartition graph can be incredibly useful for parents and researchers alike. By visualizing parenting methods, we can better assess their impact on children, compare different approaches, and ultimately improve the way we raise the next generation.